Coating of Carbide Grades
Most carbide inserts and solid carbide tools are coated with a thin layer of 3 to 20 microns (0.0001-0.0007″). The coating is typically composed of a series of sub-layers composed of mostly titanium nitride, aluminum oxide, and titanium carbon nitride. This thin layer directly enhances the performance of the inserts by increasing their hardness and insulating the heat generated from the cut to the substrate.
Coating Technologies:
CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) –

As its name suggests, in this process the coating forms a chemical bond with the substrate. Therefore, the adhesion to the substrate is very strong. With CVD it is possible to create a thick coating of 5 to 25 microns. Due to its thicker layer, CVD provides excellent heat insulation and enables achieving higher cutting speeds compared with PVD. The downside is more sensitivity to cracks and fractures.
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) –
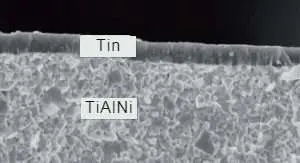
In the PVD process, the coating layer is spattered on the substrate and does not form a chemical bond with it. Therefore, the adhesion is lower, but the process induces compressive residual stress that improves the overall toughness of the carbide insert. PVD is good for creating thin coatings between 1 to 8 microns. PVD coated inserts need to operate at lower cutting speeds when compared with CVD, however, they are tougher, have a smoother surface (less friction), and can be applied also on sharper edges (small honing and ground inserts).
As a machinist, you need to understand when to prefer a thinner or thicker coating layer and when to prefer a CVD or a PVD insert!
Coating Selection Guide
| Materials | Turning | Milling |
|---|---|---|
| P | CVD | PVD |
| M | Thin CVD | PVD |
| K | CVD | PVD or Thin CVD |
| N | Uncoated | Uncoated |
| S | Thin PVD | PVD |








